Application
How to use the slides - Full screen (new tab)
Security is a matter of balance, not too much, not less. Only adequate security.

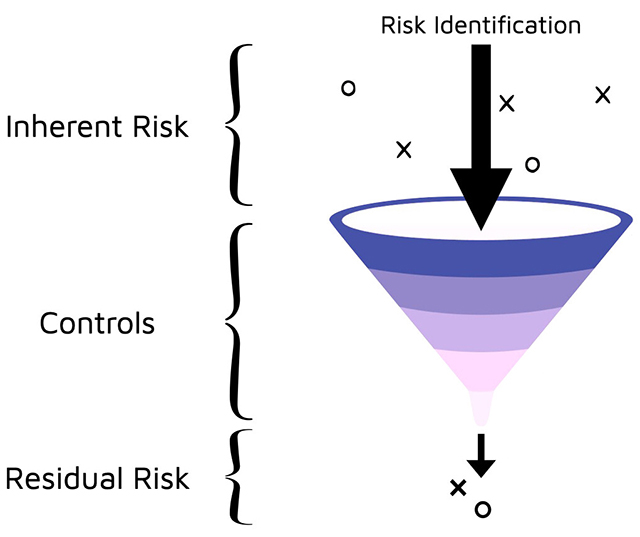
Security is about your residual risks, not what you have prevented.
Application Security
Overview
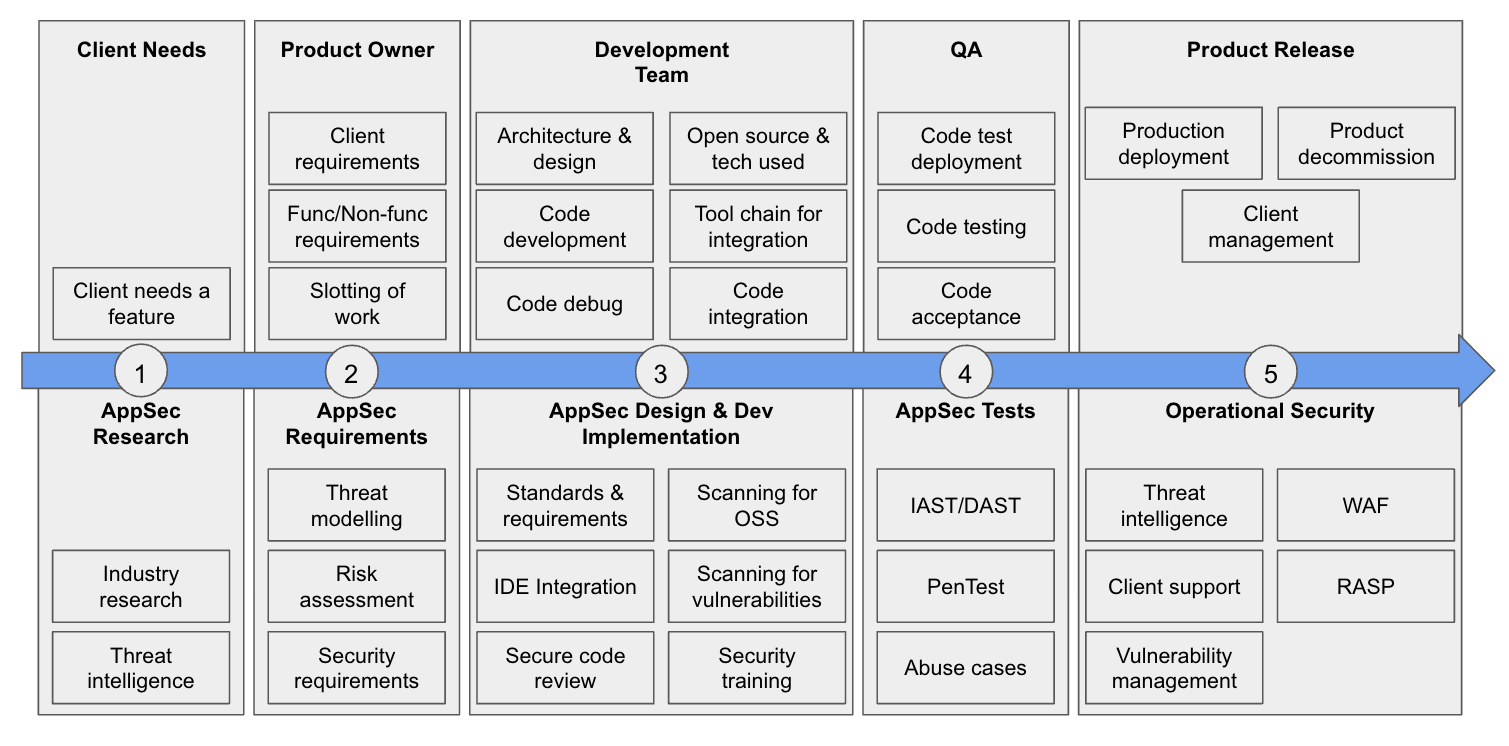
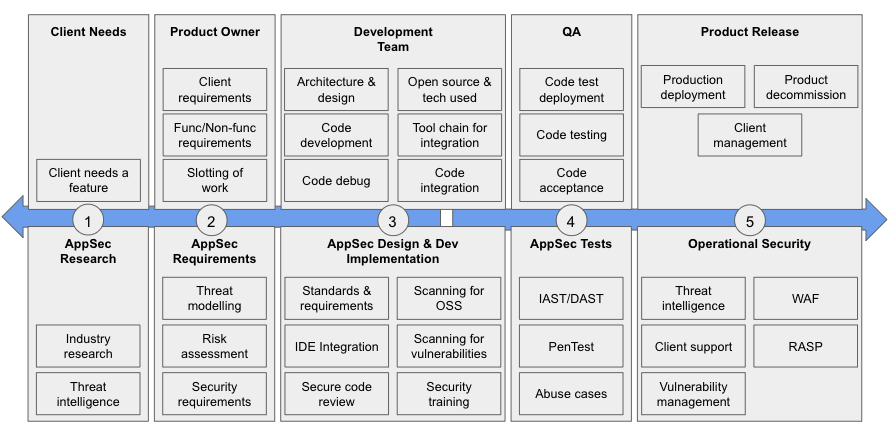
Securing SDLC
The Big Picture of AppSec
We will visit this picture multiple times.
Security Enforced Through Controls
Controls must be:
- Designed
- Developed
- Implemented
- Configured
- Operated
- Monitored
- Improved
How do we decide on Controls?
The likelihood of a threat exploiting a vulnerability and thereby causing damage to an asset.

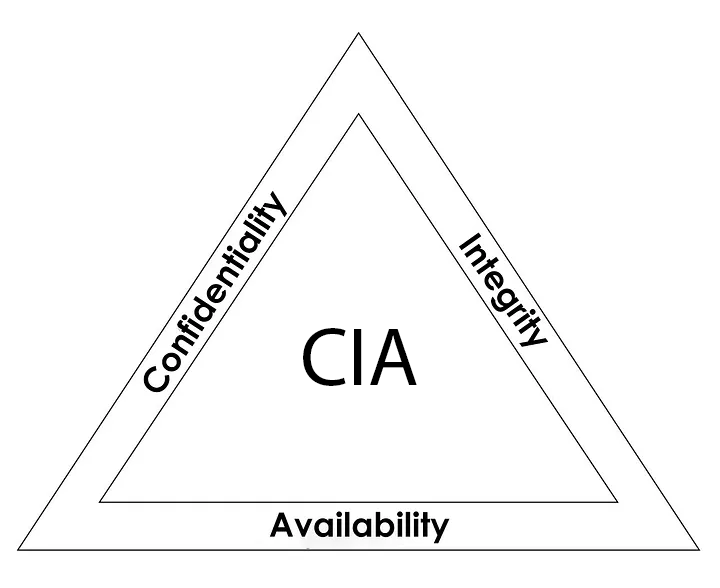
ICYMI: The CIA Triad
Things to Ensure
- Confidentiality: Ensure that only authorized people can access their authorized entities.
- Integrity: Ensure that only authorized changes are made by authorized entities.
- Availability: Ensure that the data will always be available when it is required.
The AAA + NR
- Authentication: Who you are
- Authorization: What you allowed to do
- Accountability: Who is responsible
- Non-Repudiation: Can't deny your involvement
Appsec Design Principles
In Brief
Good Enough Security
Don’t spend $10.000 on a safe to protect a $20 bill

Least Privilege
Don't give your safe's key to everybody, give only what they need

Separation of Duties
Don't give the power of creating invoices, approving invoices and sending money to one person

Defense in Depth
A castle has a moat, thick walls, restricted access points, high points for defense, multiple checkpoints inside etc.; what do you have?

Fail-Safe
Any function that is not specifically authorized is denied by default

Economy of Mechanism
Security is already a complex topic, don’t make it more complicated (KISS)

Complete Mediation
Every critical operation must have verification at every time.

Open Design
Don't even try: Security over obscurity

Least Common Mechanism
Is like the rarest key that opens specific locks, not used often but still can cause significant damage when it does.

Psychological Acceptability
There is no point if users cannot use your security controls seamlessly.

Weakest Link
A chain is only as strong as its weakest link

Leverage Existing Components
Fewer components, fewer attack surface, but more;

Single Point of Failure
If SPoF fails, means the entire system fails

Securing Software is Very Simple(!?)
- Identify Attack Surfaces What potential surfaces do you have?
- Identify Attack Vectors What potential vectors do you have?
- Allocate Security Controls Risk based approach + Security Controls
Security Controls are Easy(!?)
Security controls can be;
- Directive (Safeguard [Proactive] - means before the incident) * The policy is an example. This is what you are allowed to do, or you are not allowed to do

Security controls can be;
- Deterrent (Safeguard [Proactive] - means before the incident)
- Discourage somebody from doing something wrong. For ex. watching people with a security camera. Once they know they are under observation, they will hesitate.
Deterrent

Security controls can be;
- Preventive (Safeguard [Proactive] - means before the incident) * Try to stop a person from doing something wrong. For ex. Password is a preventive control.

Security controls can be;
- Detective (Countermeasures [Reactive] - means in the incident moment or afterwards) * Trying to detect an incident. For ex. logs

Security controls can be;
- Corrective (Countermeasures [Reactive] - means afterwards) * Tries to reestablish control after an incident and correct the immediate problem.

Security controls can be;
- Restoration/Recovery (Countermeasures [Reactive] - means afterwards) * Try to rebuild and get back to normal.

Implementation is tough, sorry
- Secure coding practices
- Separation of environments
- Proper testing
- Validation and discovery
- Mitigation
- Root cause analysis
- Documentation in every steps
Components of AppSec
- Threat Modelling: Manuel or Automated
- Security Testing: SAST, DAST, IAST, SCA, RASP
- Vuln. Collection & Prioritization: Jira, Asana
There will be blood (risk), you need to manage the blood. But how?

Risk Management but how?
- Risk Avoidance: This approach mitigates risk by refraining from activities that could negatively impact the organization.
Risk Management but how?
- Risk Reduction: This risk management method aims to limit the losses rather than completely eradicate them. It accepts the risk but works to contain potential losses and prevent their spread.
Risk Management but how?
- Risk Sharing: In this case, the risk of potential loss is distributed among a group instead of being borne by an individual.
Risk Management but how?
- Transferring Risk: This involves contractually shifting risk to a third party. For instance, insuring against property damage or injury transfers the associated risks from the property owner to the insurance company.
Risk Management but how?
- Risk Acceptance and Retention: After applying risk sharing, risk transfer, and risk reduction measures, some risk inevitably remains, as it's virtually impossible to eliminate all risks. This remaining risk is known as residual risk.
Vulnerability Disclosure Program vs Bug Bounty
Shifting Left vs Right
Known Attack Surfaces and Vectors
Known Rust Vulnerabilities
- Rust-specific issues
- Unsafe code
- Cryptographic errors
Known Substrate Vulnerabilities
- Insufficient testing
- Centralization vulnerabilities
- Pallet-specific vulnerabilities
Known ink! Vulnerabilities
- Incorrect access control
- Denial-of-Service (DoS)
- Timestamp dependence
- Outdated version
Summary: Do the damn input validation, good to go!

Question: How would you defend a castle if there is no castle to defend?