Cybersecurity Overview
How to use the slides - Full screen (new tab)
Cybersecurity Overview
Outline
- Threat landscape
- Risk management
- Development
- Conclusion
- Q&A
Notes:
- Threat landscape
- Key threat actors
- Largest crypto heists
- Crypto incidents
- Risk management
- Inherent & Residual
- Key steps of an attack
- Importance of culture
- Development
- Development and key focus
- CI/CD
- Conclusion
- Q&A
Cyber Threat - 6 Main Actors

Notes:
Different actors with different drivers but commonalities on modus operandi.
Largest Crypto Losses
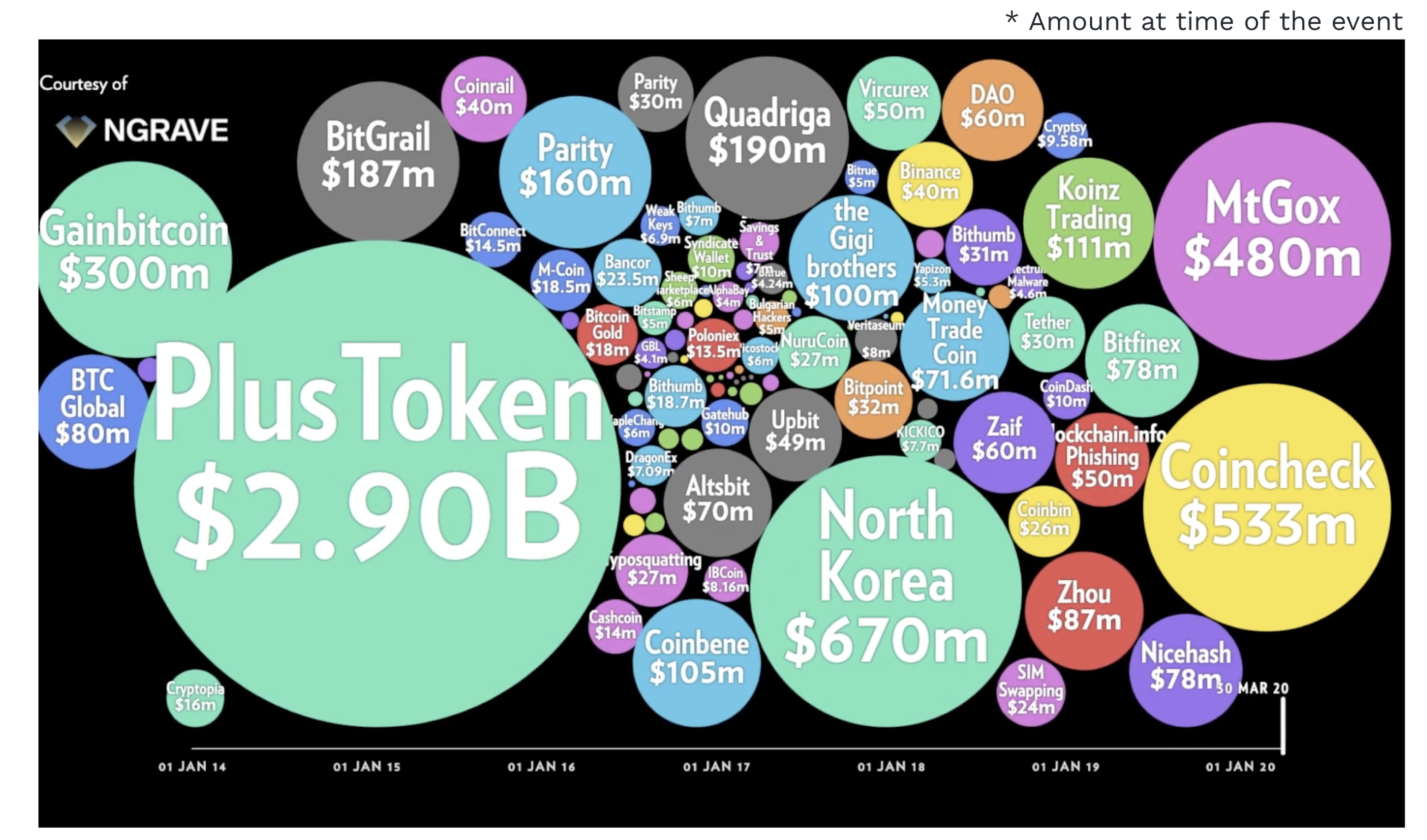
Some were Ponzi schemes, most were breaches/exploits
Notes:
On the crypto ecosystem there have been number of cyber events! https://medium.com/ngrave/the-history-of-crypto-hacks-top-10-biggest-heists-that-shocked-the-crypto-industry-828a12495e76
More Recent Crypto Incidents

Strong cyber control foundation decrease exposure to incidents.
Notes:
- https://www.forbes.com/sites/ninabambysheva/2022/12/28/over-3-billion-stolen-in-crypto-heists-here-are-the-eight-biggest/?sh=5d411c13699f
- https://www.zdnet.com/article/iota-cryptocurrency-shuts-down-entire-network-after-wallet-hack/
- https://news.bitcoin.com/kucoin-boss-on-strategy-after-hack-we-chose-to-act/
- https://www.halborn.com/blog/post/explained-the-ronin-hack-march-2022
- https://www.bitdefender.com/blog/hotforsecurity/cryptocurrency-monero-website-hacked-original-binaries-replaced/
- https://www.coindesk.com/markets/2020/02/10/new-crypto-exchange-altsbit-says-it-will-close-following-hack/
- https://peckshield.medium.com/akropolis-incident-root-cause-analysis-c11ee59e05d4
- https://www.coindesk.com/markets/2020/12/21/bitgrail-operator-may-have-hacked-own-exchange-to-steal-120m-police-allege/
- https://coinmarketcap.com/academy/article/bitgrail-hack-one-of-the-largest-crypto-hacks-in-history
- https://www.coindesk.com/tech/2020/04/08/hacker-exploits-flaw-in-decentralized-bitcoin-exchange-bisq-to-steal-250k/
- https://www.coindesk.com/policy/2021/02/20/cryptopia-exchange-currently-in-liquidation-gets-hacked-again-report/
- https://bravenewcoin.com/insights/cryptopia-exchange-liquidator-releases-third-report
- https://www.elementus.io/blog-post/cryptopia-hack-transparency
- https://blog.merklescience.com/hacktrack/hack-track-eterbase-cryptocurrency-exchange
- https://www.reuters.com/investigates/special-report/fintech-crypto-binance-dirtymoney/
InfoSec & Cyber Risk - Taxonomy

Notes:
When a threat is leveraging a vulnerability, the consequence is a risk. Usually Threats cannot be influenced, when vulnerabilities can be. Both Threats and Vulnerabilities are evolving over time based on multiple factors, so the importance of deploying controls to identify, prevent, detect and respond & recover against them (NIST)
Taxonomy - Threats Examples
- Cyber Criminal : In the last 12 months, cyber criminal activity +200%
- Insider / Disgruntled employee : lot of evolution on resources
- Hacktivist : Crypto projects and web3 have some detractors
- Terrorist : they are increasingly using cyber as a weapon
- Nation state : Geopolitical evolution with China, North Korean, Russia/Ukraine
- "Government" : There is lot of regulatory scrutiny on crypto area
- Media : Web3 & cryptocurrency evolutions are regularly in the media
- Competitors : Polkadot approach is a game changer
What Is Cyber Risk Management?

What Is Cyber Risk Management?
Inherent And Residual Risk
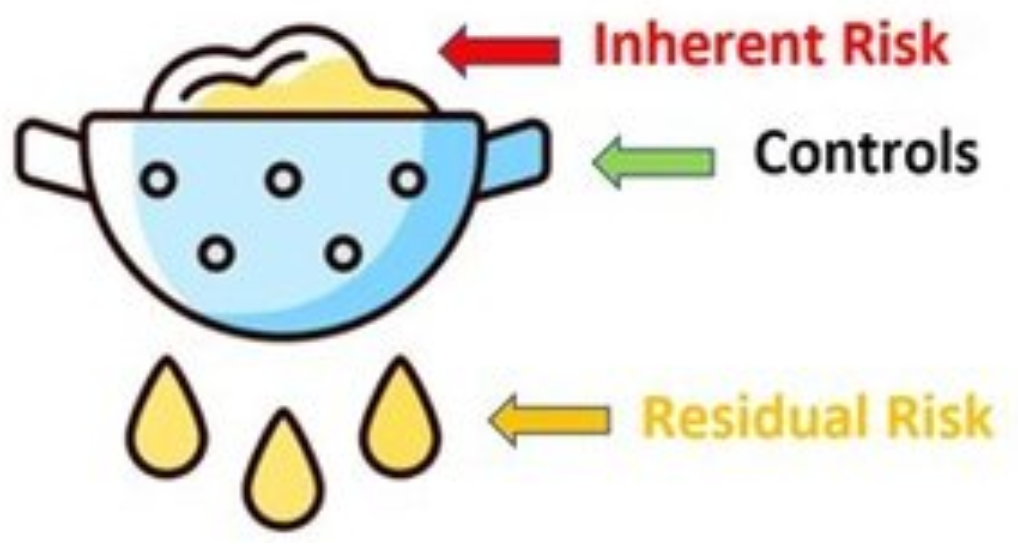
Having visibility of inherent risk facilitates a common view on area of focus and priorities.
Notes:
-
It is foundational to identify inherent risk. Including in partnership with asset owner. Especially from an impact perspective
-
Controls are key to :
- Reduce likelihood of initial compromise
- Limit the impact of compromise once a foothold has been established
And to enhance ability to detect compromise asap
Starting from the inherent risk is foundational as the threat landscape will evolve including the effectiveness of the control
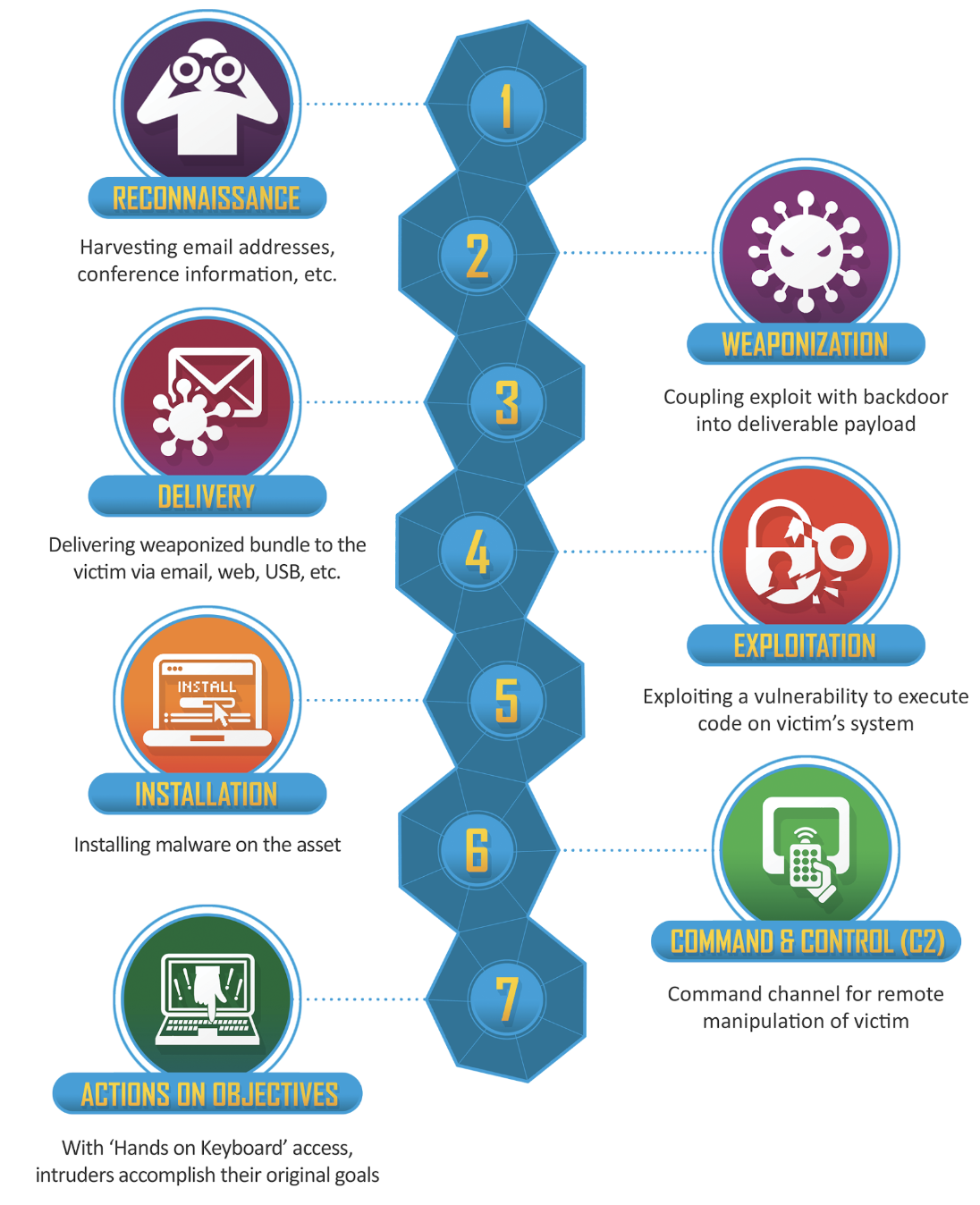
Attack Kill Chain
Notes:
Usually an attacker is not attacking directly the target but :
- Collect information leveraging the digital footprint available (linkedin profile, dns records, website, repositories, 3rd parties, anything publicly available)
- Use information available and vulnerabilities to create a “weapon” to prepare an attack
- Deliver the “weapon” via available channels : email (prof./person.), usb, WhatsApp/Signal/Telegram, webpage (legit or squatting), code update, etc
- Use the “weapon” delivered on the victim’s system to execute code
- Get a foothold on the target
- Move laterally smoothly to reach the target objective including staying hidden for a period of time
- Execute final objective : ransom, denial or service, data exfiltration, corruption, fund stealing
Importance Of Culture

InfoSec & Cyber Risk - Embedded
Security embedded and partnering at each steps with key success factors:
- Upfront threat modeling
- Peers code review
- Code scanning
- Independent security code review
- Penetration testing (pentest)
- Secret management
- Supply chain management
- Monitoring
- Playbooks
InfoSec & Cyber Risk - CI/CD
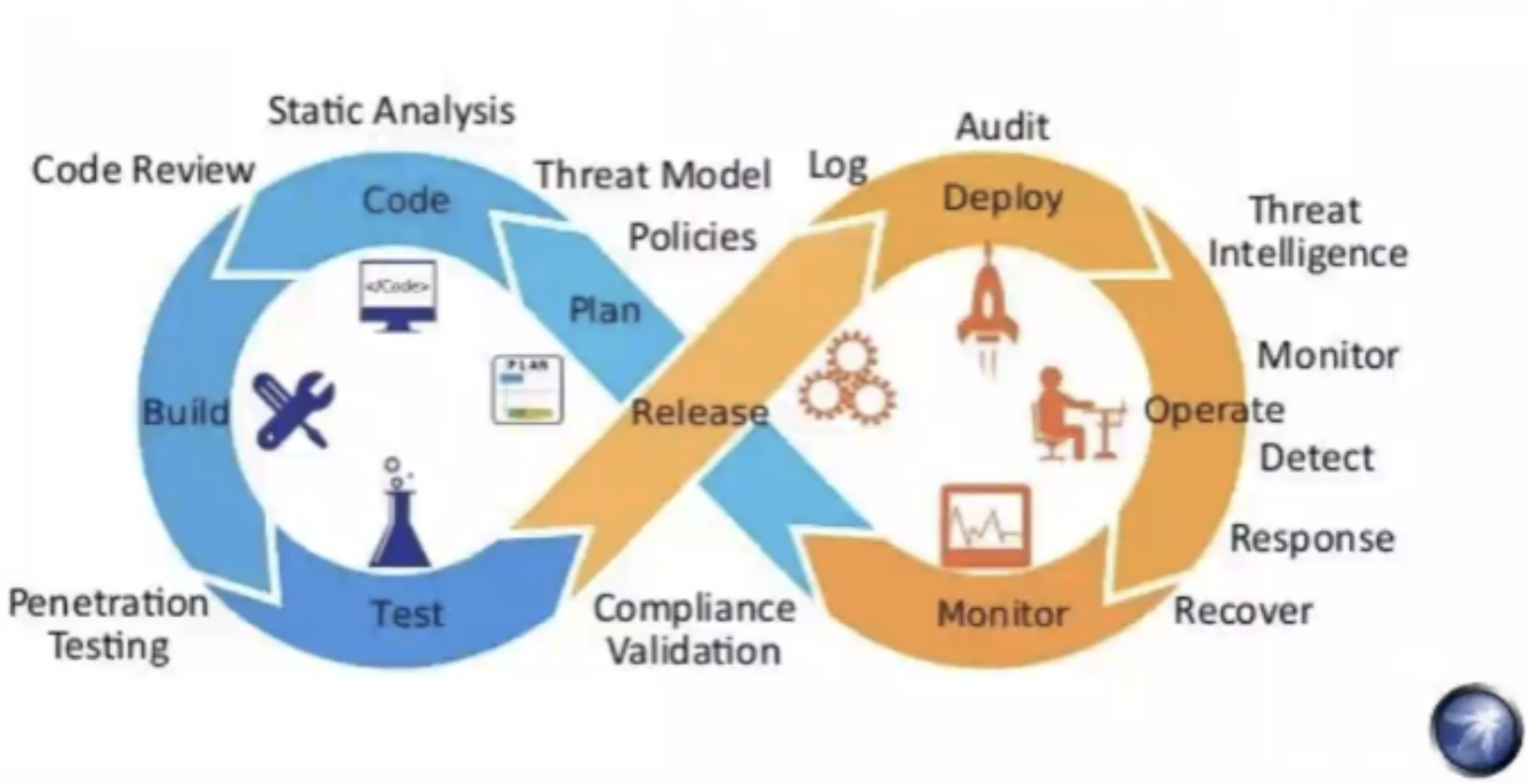
Notes:
This is a continuous process, at each step.
Conclusion

Questions
Next Practical Sessions
- Security Awareness (40/50mn) : Context and adversaries, Attack Surface and Social Engineering
- User Centric Security in Web3 (40/50mn) : Wallet landscape, Key management and User device protection
- Infrastructure Security (40/50mn) : Concentration, deplatforming, supply chain risks, Key management on the nodes and Passwords management for Infrastructure
- Application Security (60mn) : Securing SDLC, Components of AppSec and Known Attack Surfaces & Vectors
Appendix - Streetlight Effect
